As a precision maintenance coding and reporting tool, VMRS provides a scalable, manageable analytics solution for fleets.

VMRS: A Brief Overview
Vehicle Maintenance Reporting Standards (VMRS) have been around since the 1970s. Although first implemented for heavy-duty vehicles primarily in the trucking industry, VMRS has now been adopted by fleets running all Classes of vehicles across multiple industries.
But what is VMRS? Simply put, VMRS is an established coding convention that provides a universal line of communication (or language) between fleet managers, technicians, OEMs, those responsible for purchasing and/or maintaining equipment and more.[1] This "language" is then used as a tool for maintenance categorization.
Code Keys: A Numerical Breakdown
VMRS revolves mostly around a numerical system, although certain manufacturer brand or work accomplished codes will contain letters. Because vehicle technology continues to progress, VMRS codes are updated periodically by the American Trucking Associations’ (ATA) Technology and Maintenance Council (TMC) to stay current. This includes such updates as adding codes for electric vehicle (EV) powertrains. VMRS can even be scaled based on the information you want to include or exclude.
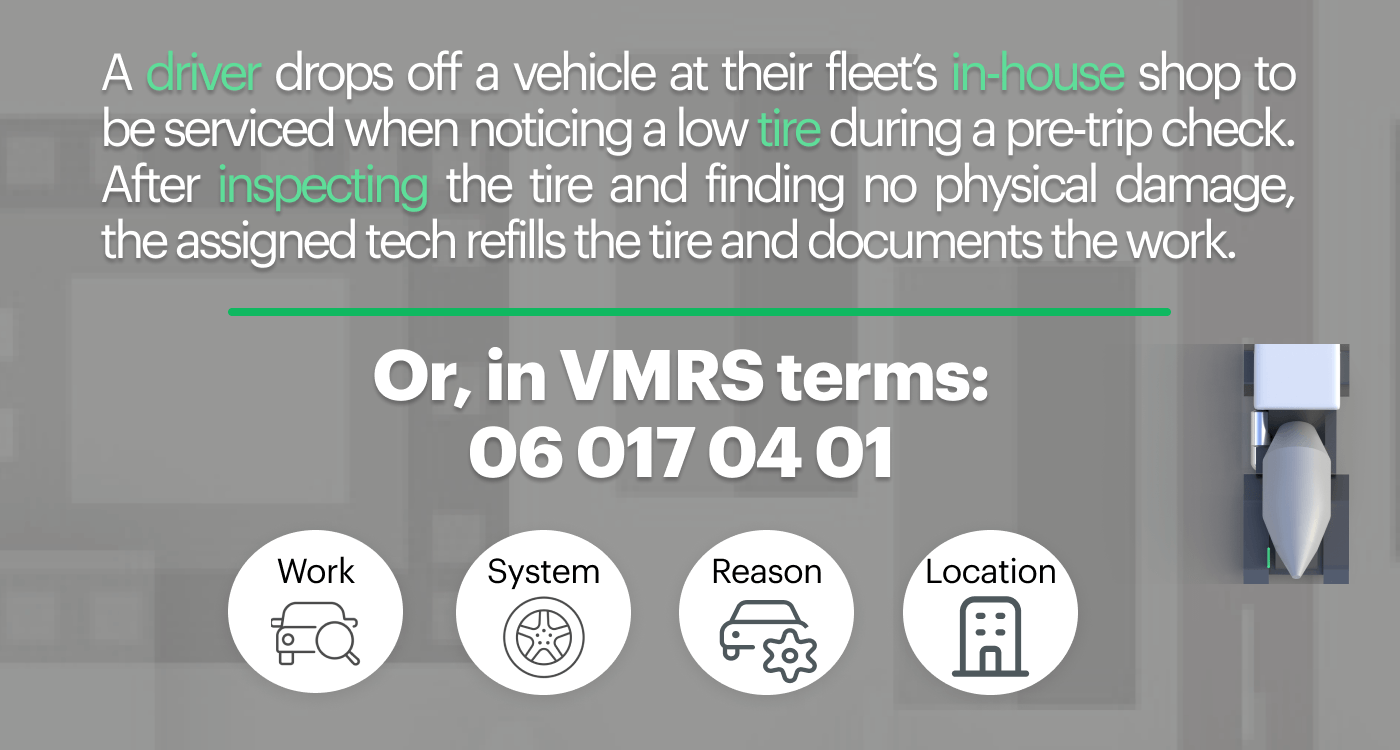
Let’s go ahead and break down one of the major Code Key segments—the parts-related codes:
-
Code Key 31—System: Code Key 31 is the first part in a 3-6-9 numerical grouping that specifies a vehicle component. Code Key 31 itself establishes the vehicle system in question; for example, code 001 equates to the air conditioning, heating, and venting system, whereas code 013 corresponds to the braking system.
-
Code Key 32—Assembly: The second three numbers in the 3-6-9 grouping give the assembly information, or sub-system. This pinpoints more specifically the location within the system. For example: 013-001 specifies braking system-front brakes and drums, whereas 013-002 specifies braking system-rear brakes and drums.
-
Code Key 33—Component: The final set of data in this segment, or Code Key 33, is the component data. Not to be confused with a manufacturer’s part number, this three digit code is a universal identifier of parts, solutions, additives, lubes, oils, and other miscellaneous components. For example, 043-001-053 indicates a diesel particulate filter.
These Code Keys can be used individually or together depending on the specificity of reporting desired. According to TMC, "VMRS can be used at any level, from total operating systems down to the individual part level. The level of coding used is entirely up to the user. No matter which level the user selects, the data collected can be compared directly to data collected by others at the same or higher VMRS coding level."[1] This provides a lot of flexibility when it comes to initial VMRS implementation, as well as data collection from third-party maintenance providers.
Know Your Codes
On their own, the above codes offer very little information in the way of work performed or actual maintenance needs. Additional Code Keys indicate reasons for repair, work accomplished and more. These codes are especially useful for technicians, who are able to save time and more accurately report work orders, faults and repairs:
-
Code Key 14—Reason for Repair: Divided into the subcategories of maintenance, management decision and outside influence, Reason for Repair codes indicate why the asset has been sent to the shop (e.g. 01-breakdown, 22-conversion, 37-vandalism).
-
Code Key 15—Work Accomplished: Techs can enter this two-digit code to specify what work was completed (e.g. 03-replace new, 06-inspect, 14-install, 17-add fluids).
-
Code Key 18—Technician Failure: Techs can enter in a two-digit code corresponding to the reason the part in question failed, or the reason the tech believes it failed (e.g. 10-bent, 22-misaligned).
There are still other codes identifying additional information, such as asset vocation and body type, repair site, repair priority and more. For a more in-depth look, visit TMC’s VMRS Overview page.
VMRS for Maintenance
Although developed for the trucking industry, VMRS has transformed over the years to reflect other industries’ use of the code system. VMRS™️ Version 2.0 is the latest version and includes updates to accommodate construction, transit and off-highway industries. So why are so many fleets across so many industries using it? Efficiency.
Using VMRS means everyone from drivers, service writers and techs to accountants and board members will be "speaking the same language" regarding fleet asset maintenance.
The Future of VMRS in Fleetio
Because it’s such a precision tool, we’re excited to announce we will be adding VMRS maintenance coding and reporting to Fleetio’s list of capabilities. This will allow both existing VMRS users and those who wish to begin using VMRS to gain more precise, real-time insight into both in-house and outsourced maintenance.
Fleetio’s VMRS solution is scalable to meet the needs of your fleet, so you get exactly the data you need without having to wade through extraneous information. Here are a few key features of our VMRS solution:
-
Control over coding depth: As mentioned, VMRS is scalable, so you can control how much of the 3-6-9 Code Key segment your fleet utilizes. Additionally, with code visibility settings, you know only the codes you need are being used. This helps keep the implementation process smooth and keeps new VMRS users from getting overwhelmed.
-
Outsourced Maintenance: Fleets outsourcing maintenance can run transactions through Fleetio’s Maintenance Shop Integration (MSI), which will automatically transcribe the transactions into VMRS coding and categorize it accordingly.
-
In-house Maintenance: Fleets servicing assets in-house can select VMRS codes directly in Fleetio’s web or mobile interface through Work Orders.
-
Reporting: VMRS reporting will include scheduled vs. unscheduled maintenance, reason for repair and part information (system assembly component).
Breaking down maintenance costs by priority can help you identify where you can optimize processes for higher return on investment (ROI), while maintenance categorization by repair reason can help you identify specific cost accumulation areas, such as preventive maintenance or outside influence. By adding VMRS capabilities to Fleetio’s platform, we aim to provide customers deeper maintenance tracking and analysis capabilities to improve overall uptime and fleet performance.
Find out how Fleetio can help you stay on top of your fleet maintenance needs. Start your free trial or request a demo of Fleetio today!